What is a bladder infection?
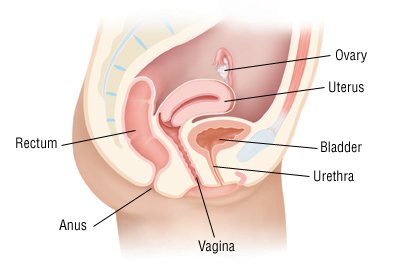
What causes a bladder infection?

According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases , most bladder infections are caused by Escherichia coli.This type of bacteria is naturally present in the large digestion tracts. An infection may happen if there are an excessive number of bacteria in the body or on the off chance that they are not eliminated through urination.
Who is at risk for a bladder infection?
Anyone can get bladder infections, yet women are more inclined to getting them than men. This is because women have shorter urethras, making the path to the bladder easier for bacteria to reach. Females' urethras are also located nearer to the rectum than men's urethras. This means there is a shorter distance for bacteria to travel.
Different factors can increase the risk of bladder infections for both men and women. These include
- Advanced age
- Stability
- Deficient liquid intake
- Surgical system inside the urinary tract
- A urinary catheter
- Urinary check, which is a blockage in the bladder or urethra
- Urinary tract abnormality, which is caused by birth deformities or wounds
- Urinary maintenance, which means trouble purging the bladder
- Narrowed urethra
- Enlarged prostate
- Entrail incontinence
- Pregnancy
- Diabetes
What are the symptoms of bladder infection?
The symptoms of a bladder infection vary contingent upon the seriousness. You'll immediately see changes amid urination. As the infection advances, pain also happens.
The absolute most basic symptoms include
- Cloudy or bloody urine
- Urinating more frequently than expected
- Foul-smelling urine
- Pain or Burning while urinating
- A frequent sensation of having to urinate, which is called urgency
- Cramping or Pressure in the lower abdomen or lower back
Bladder infections can also cause back pain. This pain is associated with pain in the kidneys. Not at all like muscular back pain, you may encounter pain on both sides of your back or the center of your back. Such side effects mean the bladder infection has likely spread to the kidneys. A kidney infection can also cause a low fever.
How is a bladder infection treated?
Bladder infections are treated with physician recommended medications to slaughter the bacteria and diminish pain and consuming. Home treatments may also help ease side effects and cure the infection.1.Medication

Oral antibiotics are utilized to slaughter the bacteria that are causing the bladder infection. In case you're encountering pain and consuming sensations, your specialist may also endorse medication to calm those side effects. The most well-known medication for easing the pain and consuming associated with bladder infections is called phenazopyridine .
2.Home treatment

A lot of liquids can help flush the bacteria out of your bladder, however water is ideal. Your specialist may suggest that you take over-the-counter vitamin C .or drink cranberry juice to increase the acid levels in your pee, which murders the bacteria. Another advantage of cranberry juice is that it keeps bacteria from adhering to the bladder walls.
Best Remedies for Bladder Infections

Why it waters- Flushes out the bacteria in your bladder, eliminating the infection faster. It also weakens your pee, so urination may be less painful. Pee is made of waste items and acids from your body. Concentrated, dark pee is more acidic and is now and again more painful to pass when you have a bladder infection. Weakened pee is lighter in shading and usually doesn't consume to such an extent.
Do This
Drink at least 10 glasses of water each day. You ought to also avoid caffeinated drinks, including espresso, tea, and soda. Caffeine can irritate your bladder considerably more when you have an infection.
2.Frequent urination

Why it frequents- Urination eliminates the infection by moving bacteria out of the bladder."Holding it,"or not setting off to the bathroom when you have to, allows bacteria to keep duplicating inside in the bladder. It's especially important to urinate after having sex. Sexual activity can push bacteria more profound into the urethra of both men and ladies. Urinating not long after sex flushes bacteria away from your urinary tract, keeping the germs from settling and causing an infection.
Do This
Drink a lot of liquids so you can urinate, and go to the bathroom as soon as you can.













