With our exceptional concentrate on macronutrients, eating less and prepared sustenance utilization in the course of recent years, muscle to fat ratio ratios levels have likewise expanded. At the end of the day, more data, additionally counting calories, more garbage sustenance has given us more fat.
What is fat loss?
We store fat in fat tissue in our bodies — for the most part under the skin (subcutaneous) or in the body hole (instinctive), with a little sum in our muscles (intramuscular). Muscle to fat ratio ratios is a vitality stockpiling warehouse.
At the point when the substances giving vitality wind up plainly scanty in your circulation system, the body recognizes this and approaches fat stores for reinforcement.
Fat storage and energy
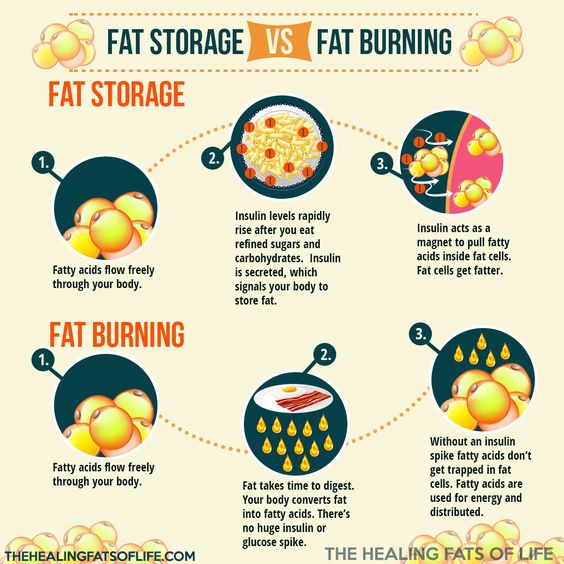
Fats are put away as triglycerides in fat cells and are discharged by means of the action of a compound known as hormone-delicate lipase (HSL). This enables fatty acids to enter the blood, where they flow bound to a protein called egg whites and enter muscles to be "singed." "Consuming" of fat is otherwise called beta-oxidation.
Tissues can separate fatty acids by method for this beta-oxidation. The procedure of beta-oxidation at last creates ATP, which is the vitality hotspot for cells. This happens in the mitochondria. Fatty acids enter the mitochondria by means of carnitine.
At the point when high measures of fatty acids are being separated and surge the mitochondria (as in starvation), there might be no prompt requirement for them. For this situation, they shape vitality rich sections known as ketones. This is vital, as fat can't be changed over into glucose, however it can give fuel to the muscle and cerebrum as these ketones.
ATP created from the breakdown of fat is utilized for metabolic procedures in the body including breathing, body temperature control, absorption, and discharge. Very still and low power work out, we get around 70% of the ATP created from fats.
Why is fat loss so vital?
As a group, people in most industrialized societies are likely to be over-fat.
This isn’t just a cosmetic problem. Excess body fat can negatively affect nearly every facet of life, including:
- decreased mobility
- poorer emotional health and self-esteem
- increased risk of organ failure
- poorer circulatory health
- increased risk of heart disease
- increased risk of stress fractures
- increased risk of strokes
- increased risk of cancers
- decreased sexual and reproductive health
Fat cells can act as endocrine factories and produce hormones that influence numerous processes in the body most of which lead to more fat accumulation.
Beyond the health of it all, carrying a lower body fat is often considered more attractive and desirable as the underlying musculature is revealed.
Further, carrying a lower body fat is advantageous for many sport competitors (barring sumo wrestlers, linemen, etc) as extra fat weight adds drag and additional resistance that must be overcome.
Bottom line: Carrying a lot of excessive body fat makes health, body composition, and athletic performance worse.
But it's hard.
Be that as it may, here's the issue — all in all, we're bad at losing fat either.
Indeed, even present day headways in corpulence treatment (e.g., bariatric surgery, medicine, and so forth) have a win rate of under 10% for perpetual weight diminishment/administration.
Around 95% of the individuals who are overweight go on rehashed diets, just to increase most or the greater part of the weight back inside one year. Almost 70% of the United States is overweight or corpulent. The rate of 12 to 17 year olds who are overweight has multiplied since 1980.
We require a superior arrangement. Knowing how fat loss functions might be useful.
What you should know?
Fat cells are a noteworthy stockpiling site for muscle to fat ratio ratios, and are in a persistent condition of turnover. Fat digestion is managed freely by wholesome, metabolic, and hormonal elements; the net impact decides levels of coursing fatty acids and the degree of muscle to fat quotients.
Fat loss and hormones :
Fatty corrosive discharge and utilize requires bring down insulin levels and an expansion of the hormones glucagon, cortisol, epinephrine, and development hormone. These "hostile to insulin" hormones initiate HSL. The other real hormone that impacts fat digestion is thyroxine (thyroid hormone).
After a huge nourishing, glycogen is combined until stores are renewed. On the off chance that high glucose endures, glucose is changed over to fatty acids. Amino acids can likewise be changed over to fatty acids. The compound important for cells to acknowledge triglycerides is lipoprotein lipase.
In the un-encouraged state, insulin fixations fall, and the counter insulin hormones increment. This quickens fat utilize.
Fat loss and caloric shortage :
When we diminish our caloric admission essentially, the body jam fat stores effectively. Since insulin is low, thyroid hormone generation is diminished. With this, resting digestion is brought down. This can occur inside 24 hours of beginning an extraordinary eating routine.
The body's reaction to calorie hardship makes bounce back weight increase everything except unequivocal once the eating routine is disposed of. Muscle is normally lost, so the body generally winds up plainly fatter.
Fats are something other than a fuel source amid rest and lower force work out. Fats reestablish phosphagens that have been depleted amid high power work out. After serious exercise sessions, oxygen take-up is expanded, which enables reclamation to pre-practice conditions (the "afterburn" impact).
Fat loss is a perplexing issue :
With our emphasis on particular supplements, extreme sustenance guiding, eating less and handled nourishment utilization in the course of recent years, muscle to fat quotients levels have likewise expanded. As such, more data, additionally consuming less calories, more garbage sustenance has given us more fat.
While some of this may appear to be strange, it represents the significance of body mindfulness (hunger/satiety signals), shirking of handled nourishments, customary physical action and compelling sustenance publicizing.
9 Ways To Burn Fat Fast :
Implement these 9 fat-burning tips that use exercise and diet and watch the body fat melt like the butter you're no longer using
The human body is a remarkably adaptable machine. Even if years and years of neglect have allowed pound after pound of fat to fill out your frame, you can rid yourself of that lard at a much faster rate than you brought it on board. In that sense, time is your side!
Take these nine easy-to-implement tips to heart, and progress will come in a hurry!
1. Stay Off The Scale
That you can gain muscle and lose fat is one of the reasons I stress to people not to follow the scale. Body composition and how you look in the mirror matters more than what the scale says.
You could train hard and eat right and build five pounds of muscle and lose five pounds of fat, and what will the scale say? That you still weigh the same.
Frustrating, even though you've made good progress. Use the scale as a guide, but how you look in the mirror, how you feel, and how your clothes fit are much better indicators of your progress.
2. Reduce Your Calories Gradually
If you're looking to lose fat, don't make huge calorie cuts. This will kick your body into starvation mode, reducing your metabolism and making it more difficult to burn off the fat.
To prevent this metabolic slowdown and allow your body to burn fat at an optimal rate, make smaller calorie reductions every week or two.
3. Vary Your Caloric Intake
This is another way to outsmart your body and continue to lose body fat without lowering your metabolism.
By varying your caloric intake every few days instead of eating the exact same amount of calories every day, keep the starvation mechanism in check and continue to burn fat.
4. Train With Weights
Resistance training helps with fat loss in a number of ways. Weight training itself burns calories. Studies also show that, unlike aerobic exercise, weight training increases the calories you burn at rest for up to 39 hours after your workout.
Plus, the more muscle your body has, the more calories you burn each day.
Even if your goal is solely to lose body fat, you need to train with weights. This will help prevent any of the weight you lose from being muscle.
Were that to happen, your metabolism would slow, stalling your fat-loss efforts and turning you into a skinny-fat person.
Yes, even someone with anorexia can have a high body fat percentage.
5. Do High-Intensity Intervals (HIIT)
This means alternating a brief period of high-intensity exercise with brief rest periods.
The result: better results in less time.
One of my favorite interval methods is jumping rope. You may need to practice a bit on this one. After a brief warmup, I'll jump rope as fast as I can for 10-20 seconds, followed by a half a minute at a slower cadence.
Always warm up before intervals, by the way. If you're not in the best shape, start with cardio of low or moderate intensity. You might also want to check with your doctor.
6. Eat More Fat
Consuming enough of the good fats will help you lose fat, build muscle, and recover faster from your workouts. Healthy fats also have myriad health benefits, including being good for your heart.
So which fats are "good" fats? The polyunsaturated ones (especially omega-3s), such as those from fish and nuts, and the monounsaturated kind, such as those from peanut butter, olive oil, egg yolks, and fish oil.
7. Cut Carbs
The attention focused on low-carb diets has divided many people into "pro" and "anti" low-carb camps. Whichever side you're on, the bottom line is that reducing your carb intake—especially sugar and starches—when trying to lose fat will help.
Those carbs you do consume should come from sources such as oatmeal and vegetables.
The timing of your carb intake also affects fat-burning. "I recommend tapering down carbohydrates by 3 p.m.," saysTeam Bodybuilding.com member Ashley Johns, also known by the BodySpace handle Hottie-I-Am. "Consume most of your carbs in the morning and around your workouts."
8. Increase Your Protein
Increasing protein intake will increase your metabolism and help to maintain your muscle mass, all of which helps with fat-burning. In fact, your body burns more calories when you eat protein than when you digest either fats or carbs.
This may explain why the fat-burning effects of eating more protein were confirmed in a study published in the American Journal of Physiology. One group was fed a high-protein diet (just over 1 gram per pound of body weight per day) while the second group consumed an amount closer to the lower recommendation of the RDA (recommended dietary allowance). The group eating the higher-protein diet burned the most fat.
Yes, you read that right, Grasshopper: Many dieters actually gained muscle mass without working out, simply by eating a high-protein diet.
9. Eat 6 Smaller Meals Per Day, Not 2-3 Feasts
This will ensure that you supply your body with the nutrients necessary to build muscle and burn fat.
Bonus: Your resting metabolic rate increases. It will also prevent your body from kicking into "starvation" mode, which can happen when too much time elapses between meals.
If this happens, your body will start burning muscle for energy and increasing your body-fat stores, as well as slowing down your metabolism. This is the exact opposite of what you want to happen.
Don't be the kind of person who complains about your situation but never does anything to improve it. Don't become "happy" with the status quo of being miserable. Now use this knowledge to take action!
Summary and recommendations:
To maintain a low body fat and/or lower body fat:
- Exercise at least 5 hours per week
- Eat whole/unprocessed foods at regular intervals, while being aware of physical hunger/fullness cues
- Sleep 7-9 hours per night
- Don’t engage in extreme diets
- Stay consistent with your habits
- Incorporate non-exercise physical activity
- Ignore food advertising

For extra credit :
Aspartame was approved for use in 1981, and while this non-caloric sweetener was hypothesized to help control body weight, since 1980, levels of body fat have increased.
Factors associated with lower levels of body fat include:
nuts
- green tea
- low energy-density foods
- dietary protein
- avoiding refined carbohydrates
- adequate hydration
- dietary fiber
- fruits and vegetables
- regular exercise
- adequate sleep
- a supportive social network
While cortisol can break down muscle tissue, it can also break down body fat.
If you increase physical activity and nutritious food intake, metabolism will increase.
Blaming weight gain on calories is like blaming wars on guns. The diet is not the cause of excessive body fat levels. Rather, it’s the entire lifestyle.
Severe calorie deprivation inhibits the production of serotonin, a brain chemical needed to control appetite and maintain harmony with food.